MURABAHA
What is Murabaha?
Murabaha is a term that has its origins in the Arabic language and means “profit” or “gain” . In the context of Islamic finance, Murabaha is a method of financing that allows a buyer to acquire an asset, usually goods or products, without having to pay the full price at once. Instead, the buyer and seller agree on a premium price (cost plus a profit margin) that can be paid in installments.
Murabaha is widely used in the Islamic world to finance purchases of goods such as vehicles, equipment, properties, and even raw materials . It is particularly popular in commercial transactions and project financing.
How Does Murabaha Work?
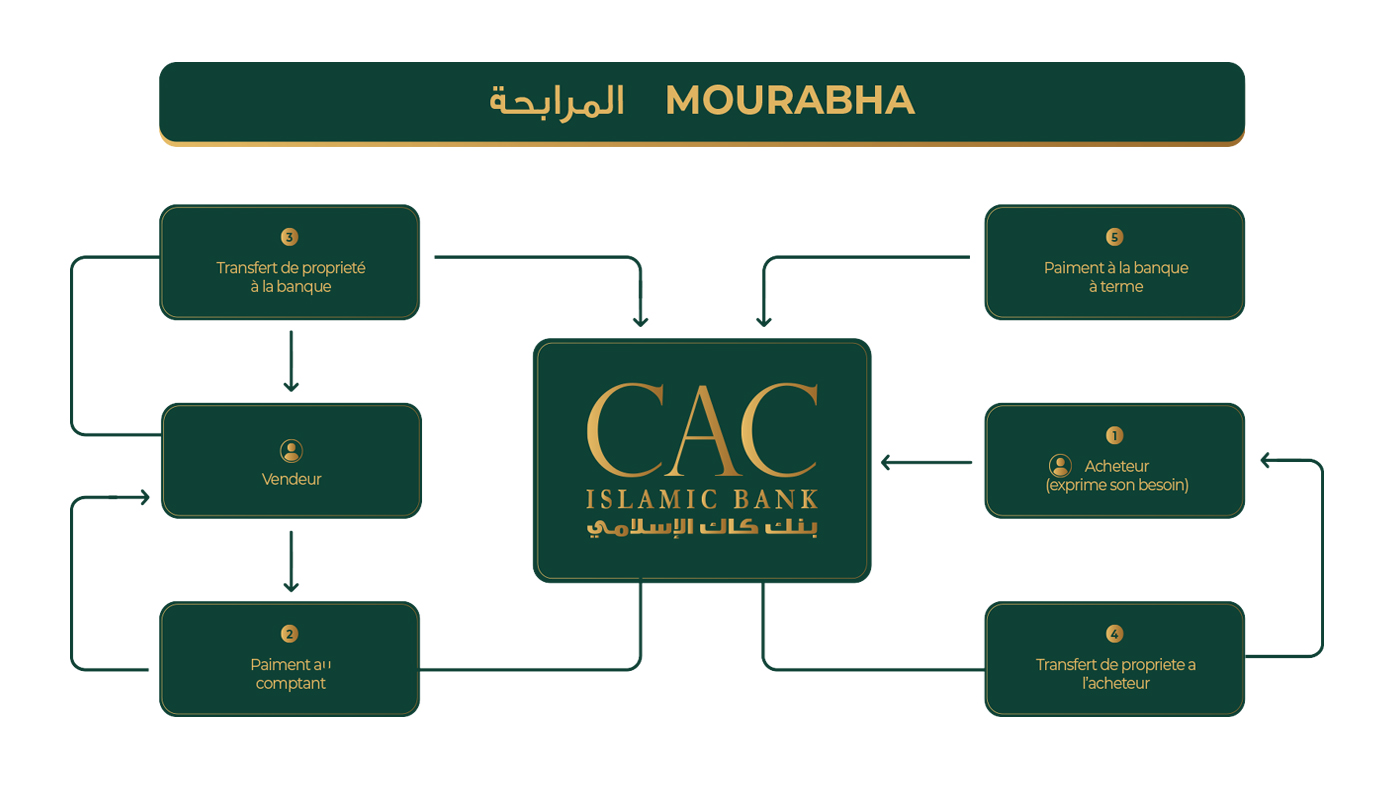
The Murabaha follows a well-defined process:
- Purchase request: The buyer expresses his intention to purchase a specific good.
- The Murabaha Contract: The buyer and seller enter into a Murabaha contract which specifies the property to be purchased, the selling price (including the seller's profit margin), the initial amount to be paid, and the terms of payment.
- Initial payment: The buyer pays an agreed-upon initial amount. This can be an advance or a deposit.
- Transfer of ownership: The property is purchased by the seller who then becomes the legal owner.
- Resale to the buyer: The seller then resells the good to the buyer at a premium price, in accordance with the Murabaha contract.
- Installment Payments: The buyer makes installment payments over an agreed period until the total plus price is paid in full.
- Final Ownership: Once all payments are made, legal ownership of the property passes to the buyer.
Main Features of Murabaha
The Murabaha has several distinctive characteristics:
- Transparency: The terms of the contract, including the seller's profit margin, should be clearly defined.
- Actual purchase: Murabaha involves an actual purchase of a good. The seller must be the legal owner of the property at any given time.
- No interest: Unlike conventional loans, Murabaha does not carry interest ( riba ), making it Sharia compliant.
- Installment payments: The option of installment payments allows the buyer to spread the cost of the item over a period, which is particularly advantageous for large purchases.
- Shared risk: Although the seller's profit margin is fixed, the risk of holding the property during the payment period is shared between the seller and the buyer.
Applications of Murabaha
Murabaha is commonly used in various fields, including:
- Financing consumer goods: Individuals can use Murabaha to finance the purchase of vehicles, household appliances, and other consumer goods.
- Real estate financing: Murabaha is used to finance the purchase of properties, allowing buyers to spread the payment over several years.
- Business Transactions: Businesses use Murabaha to purchase equipment, raw materials, and other assets needed for their operations.
- Project financing: Murabaha can be used to finance infrastructure, construction and investment projects.
- International Trade: Murabaha is also used in international trade to facilitate the purchase of products and raw materials.
Benefits of Murabaha
Murabaha has several advantages:
- Sharia Compliance: The Murabaha complies with Sharia principles, making it suitable for Muslims who are keen to uphold these principles.
- Ease of Access: It is widely used in the Islamic world and is therefore easily accessible.
- Ease of payment management: Installment payments make it easier for buyers to manage their finances.
- Versatile Application: Murabaha can be used to finance a wide range of goods and projects.
- Shared risk: Sharing the risk between the buyer and seller is a positive aspect.
Implications and Considerations
Although Murabaha is Sharia compliant, it is important to note that it is not without its critics. Some observers believe that in some transactions it may resemble disguised interest due to the structure of the profit margin. It is therefore essential that Murabaha contracts are drawn up transparently and that the parties involved act ethically.